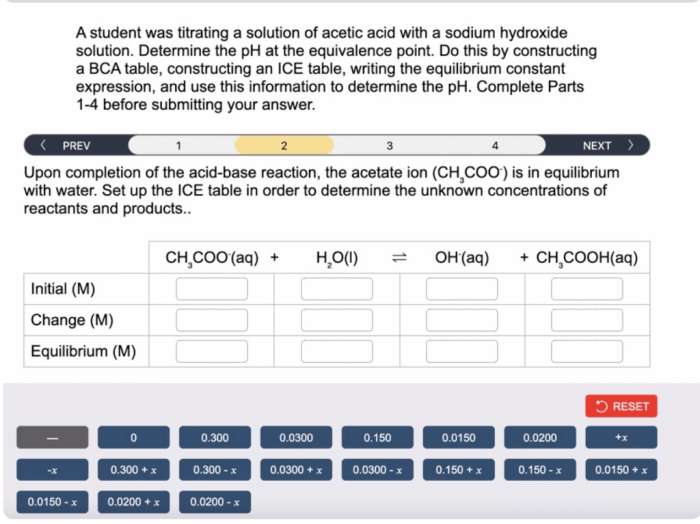
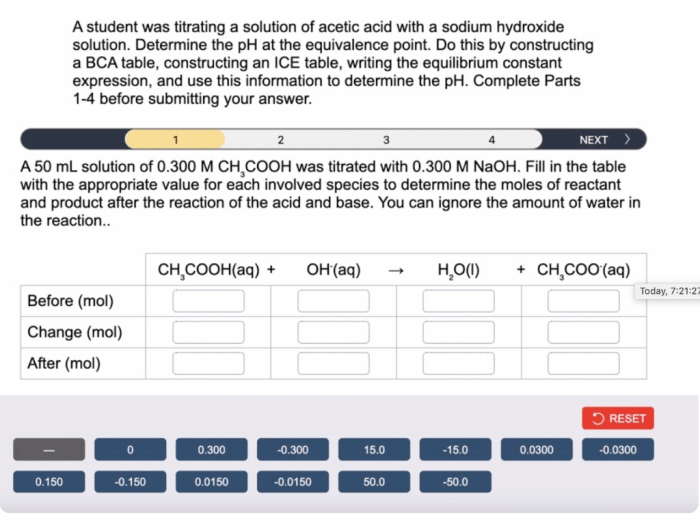
A student was titrating a solution of HC4H7O2, commonly known as acetic acid, to determine its concentration. Titration is a fundamental technique in chemistry that involves the controlled addition of a known reagent to a solution of unknown concentration until a reaction is complete.
In this experiment, the student used a burette to add a solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to the acetic acid solution until the equivalence point was reached, as indicated by a change in color of the phenolphthalein indicator.
The experiment required careful preparation and execution. The student first prepared a standardized solution of NaOH by dissolving a known mass of NaOH in water and calculating its exact concentration. The acetic acid solution was then prepared by diluting a known volume of concentrated acetic acid with water.
The student then calibrated the burette and recorded the initial burette reading.
Titration of a Solution of HC4H7O2: A Student Was Titrating A Solution Of Hc4h7o2
Introduction, A student was titrating a solution of hc4h7o2
Titration is a fundamental technique in chemistry that involves the controlled addition of a known concentration of a solution (titrant) to another solution of unknown concentration (analyte) until a chemical reaction is complete. This process allows for the determination of the concentration of the analyte solution.
In this experiment, we will focus on the titration of a solution of HC4H7O2 (acetic acid).
FAQs
What is the purpose of titration?
Titration is used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution by reacting it with a solution of known concentration.
What is the equivalence point in titration?
The equivalence point is the point at which the moles of titrant added are equal to the moles of analyte present in the solution being titrated.
What is the role of the indicator in titration?
The indicator is a substance that changes color at or near the equivalence point, signaling the completion of the reaction.