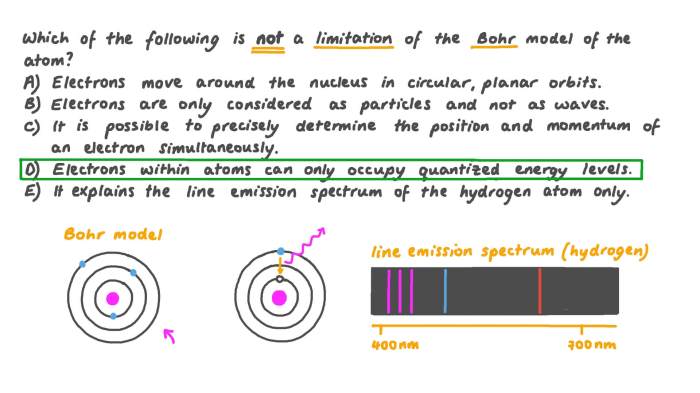
Select all the characteristics that apply to an atomic orbital. Embark on an enlightening journey into the captivating realm of quantum mechanics, where we delve into the fundamental building blocks of matter. Prepare to unravel the enigmatic properties of atomic orbitals, the cornerstone of our understanding of atomic structure and chemical bonding.
Atomic orbitals, the enigmatic electron clouds surrounding atomic nuclei, possess a unique set of characteristics that define their behavior and significance. These defining traits govern the arrangement and energy distribution of electrons within atoms, ultimately shaping the chemical properties and reactivity of elements.
Atomic Orbitals
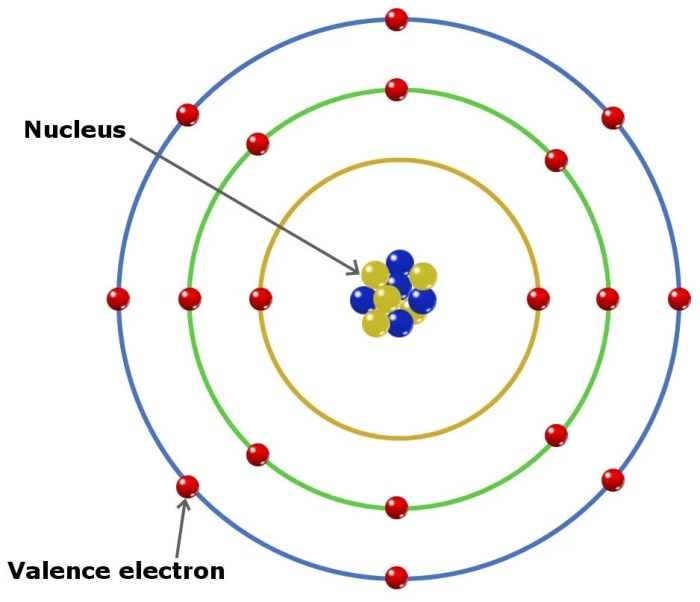
Atomic orbitals are mathematical functions that describe the wave-like behavior of electrons in atoms. They are three-dimensional regions of space where the probability of finding an electron is maximum.
Atomic Orbital Shape, Select all the characteristics that apply to an atomic orbital.
The shape of an atomic orbital is determined by the quantum numbers of the electron occupying it. The three quantum numbers are:
- Principal quantum number (n): Describes the energy level of the orbital.
- Azimuthal quantum number (l): Describes the shape of the orbital.
- Magnetic quantum number (ml): Describes the orientation of the orbital in space.
The azimuthal quantum number (l) can have values from 0 to n- 1. Each value of l corresponds to a different type of orbital:
- l = 0: s orbital (spherical shape)
- l = 1: p orbital (dumbbell shape)
- l = 2: d orbital (four-lobed shape)
- l = 3: f orbital (eight-lobed shape)
Helpful Answers: Select All The Characteristics That Apply To An Atomic Orbital.
What is the significance of atomic orbital shapes?
Atomic orbital shapes determine the spatial distribution of electrons, influencing their energy levels and chemical bonding properties.
How do energy levels affect atomic orbital occupancy?
Electrons occupy atomic orbitals in order of increasing energy, following the Aufbau principle and Hund’s rule.
What is the role of orbital hybridization in chemical bonding?
Orbital hybridization allows atomic orbitals to combine and form new hybrid orbitals with specific shapes and orientations, facilitating the formation of chemical bonds.