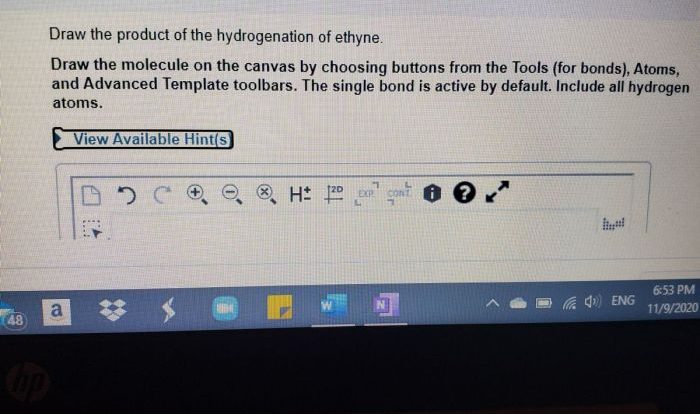
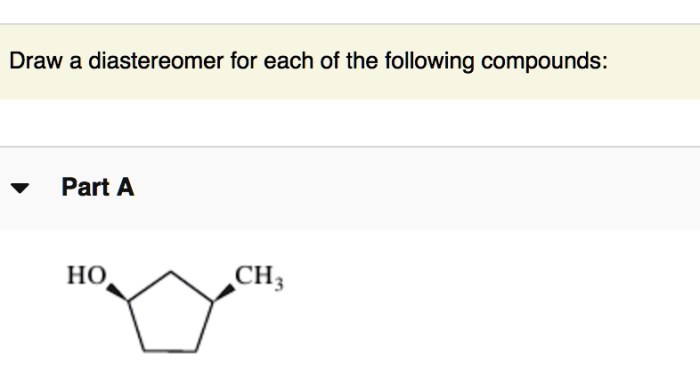
Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds – Delve into the captivating realm of diastereomers with this comprehensive guide. Embark on a journey to understand their intricacies, from their distinct characteristics to their impact on reactivity. This discourse unveils the nuances of diastereomers, equipping you with the knowledge to decipher their significance in the tapestry of organic chemistry.
This treatise unravels the intricacies of diastereomers, exploring their unique properties and the factors that govern their formation. Prepare to be captivated by the interplay of chirality and relative stereochemistry, unraveling the secrets of these fascinating molecular entities.
1. Draw a Diastereomer for Each Compound
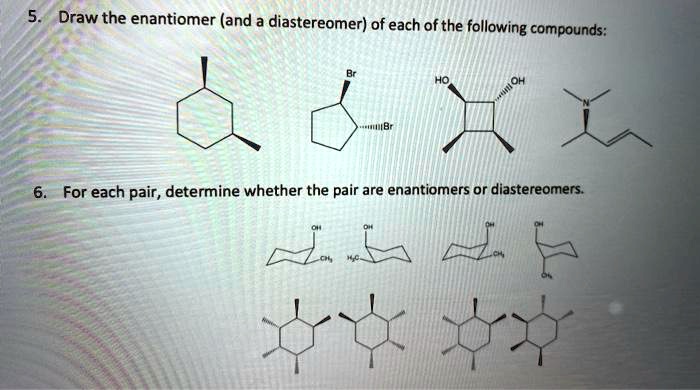
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other. They have the same molecular formula and connectivity, but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
To draw a diastereomer for a given compound, follow these steps:
- Identify the chiral centers in the molecule.
- For each chiral center, assign a configuration (R or S).
- Invert the configuration of one or more chiral centers.
- Draw the new molecule, making sure that the connectivity of the atoms is the same as in the original molecule.
For example, the compound 2-bromobutane has one chiral center. The following are two diastereomers of 2-bromobutane:
- (2R)-2-bromobutane
- (2S)-2-bromobutane
2. Identifying Diastereomers

Diastereomers are different from stereoisomers, which are molecules that have the same molecular formula and connectivity, but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms. Stereoisomers can be either enantiomers or diastereomers.
The following table compares the properties of stereoisomers and diastereomers:
| Property | Stereoisomers | Diastereomers |
|---|---|---|
| Mirror images | Yes | No |
| Physical properties | Different | Different |
| Chemical properties | Same | Different |
Diastereomers can be identified using a variety of physical and spectroscopic techniques. These techniques include:
- Gas chromatography
- Liquid chromatography
- Mass spectrometry
- NMR spectroscopy
3. Properties and Reactivity of Diastereomers: Draw A Diastereomer For Each Of The Following Compounds
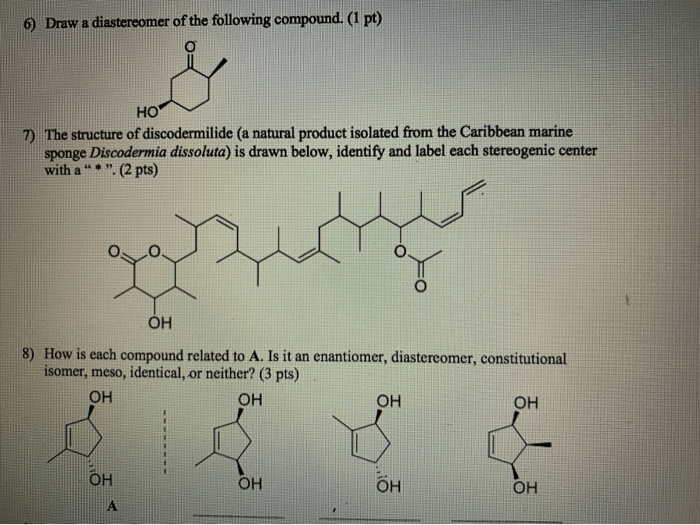
Diastereomers have different physical and chemical properties. These differences are due to the different spatial arrangement of their atoms.
The physical properties of diastereomers include:
- Melting point
- Boiling point
- Solubility
- Optical rotation
The chemical properties of diastereomers include:
- Reactivity
- Selectivity
- Stereoselectivity
The relative stereochemistry of diastereomers can affect their reactivity. For example, one diastereomer may be more reactive than another in a particular reaction.
4. Diastereoselective Synthesis
Diastereoselective synthesis is the synthesis of one diastereomer over another. This can be achieved using a variety of methods, including:
- Chiral auxiliaries
- Chiral catalysts
- Enantioselective synthesis
The factors that influence diastereoselectivity include:
- The steric effects of the substituents on the chiral center
- The electronic effects of the substituents on the chiral center
- The solvent effects
- The temperature
Query Resolution
What is the key difference between stereoisomers and diastereomers?
Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms. Diastereomers are a specific type of stereoisomer that are not mirror images of each other.
How can I identify diastereomers?
Diastereomers can be identified using physical and spectroscopic techniques. Physical techniques include melting point, boiling point, and optical rotation. Spectroscopic techniques include NMR and IR spectroscopy.
What factors influence the reactivity of diastereomers?
The relative stereochemistry of diastereomers can affect their reactivity. For example, diastereomers with bulky groups on the same side of the molecule may be less reactive than diastereomers with bulky groups on opposite sides of the molecule.