Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of AP Human Geography Unit 3 FRQ, where we unravel the intricate tapestry of human existence and its profound impact on the world around us. Delve into the fundamental concepts that shape our understanding of population, culture, environment, and development, exploring their interconnectedness and relevance to contemporary global issues.
Through the lens of human geography, we’ll uncover the diverse methodologies employed by geographers to gather and analyze data, shedding light on the strengths and limitations of each approach. Together, we’ll trace the evolution of human geography in the face of 21st-century challenges, examining how geographers are adapting their practices to address pressing societal concerns.
Define Human Geography: Ap Human Geography Unit 3 Frq
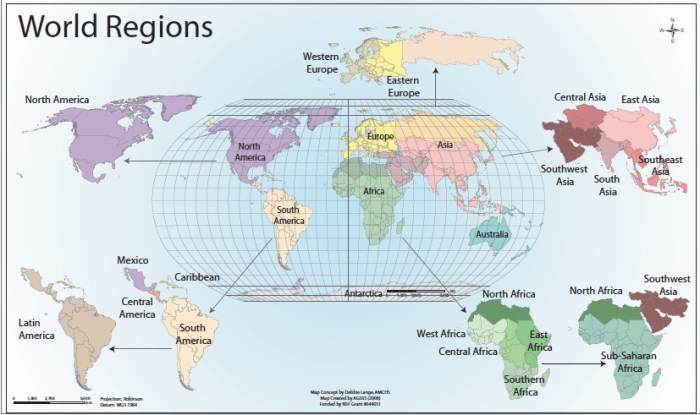
Human geography is the study of the relationship between humans and their environment. It examines how people interact with the physical world around them, and how these interactions shape the human experience. Human geography is a broad field that encompasses a wide range of topics, including population geography, economic geography, cultural geography, and political geography.Human
geography is closely related to other disciplines, such as sociology, anthropology, and economics. However, human geography has a unique perspective that sets it apart from these other disciplines. Human geographers are interested in the spatial distribution of human activity, and how this distribution affects the human experience.Human
geography is used to understand a wide range of issues, including:* The distribution of population
- The location of economic activity
- The spread of culture
- The causes of conflict
By understanding the relationship between humans and their environment, human geographers can help us to create a more sustainable and just world.
Relationship between Human Geography and Other Disciplines
Human geography is closely related to other disciplines, such as sociology, anthropology, and economics. However, human geography has a unique perspective that sets it apart from these other disciplines. Human geographers are interested in the spatial distribution of human activity, and how this distribution affects the human experience.For
example, sociologists study the social interactions between people, while anthropologists study the culture of different societies. Economists study the production and distribution of goods and services. Human geographers, on the other hand, are interested in how these different factors interact with the physical environment to create the human experience.
Examples of How Human Geography is Used to Understand the World Around Us
Human geography is used to understand a wide range of issues, including:* The distribution of population: Human geographers study the distribution of population around the world. They are interested in why people live where they do, and how population distribution affects the human experience.
The location of economic activity
Human geographers study the location of economic activity around the world. They are interested in why businesses are located where they are, and how the location of economic activity affects the human experience.
The spread of culture
Human geographers study the spread of culture around the world. They are interested in how culture is transmitted from one place to another, and how culture affects the human experience.
The causes of conflict
As you delve into the complexities of AP Human Geography Unit 3 FRQ, consider exploring the diverse perspectives at the TN FFA State Convention 2023 . Engage with experts, attend workshops, and witness firsthand the real-world applications of geographic principles.
Return to Unit 3 FRQ with a renewed understanding of the interconnectedness of human societies and their environments.
Human geographers study the causes of conflict around the world. They are interested in why conflicts occur, and how the location of conflict affects the human experience.By understanding the relationship between humans and their environment, human geographers can help us to create a more sustainable and just world.
Describe the Major Themes of Human Geography
Human geography is a branch of geography that studies the relationship between humans and their environment. It encompasses a wide range of topics, including population, culture, environment, and development. These themes are interconnected and shape the human experience in various ways.
Population
Population geography examines the distribution, density, and composition of human populations. It investigates factors that influence population growth, such as birth rates, death rates, and migration patterns. Understanding population dynamics is crucial for addressing issues like urbanization, food security, and resource allocation.
For instance, rapid population growth in developing countries can strain resources and infrastructure, while declining populations in developed countries can lead to labor shortages and economic challenges.
Culture
Cultural geography explores the diverse cultures of the world, including their languages, religions, customs, and values. It examines how culture influences human behavior, shapes landscapes, and fosters a sense of identity and belonging.
For example, cultural differences can impact communication, conflict resolution, and economic practices. Understanding cultural diversity is essential for fostering tolerance, promoting intercultural dialogue, and preserving cultural heritage.
Environment
Environmental geography focuses on the interaction between humans and their physical environment. It investigates how human activities impact the environment and how environmental factors shape human societies.
For instance, climate change, deforestation, and water pollution are pressing environmental issues that have profound implications for human health, livelihoods, and well-being. Understanding environmental geography is crucial for developing sustainable practices and mitigating the impacts of human activities on the planet.
Development
Development geography examines the processes and patterns of economic, social, and political development around the world. It investigates factors that contribute to development, such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and governance.
For example, disparities in development levels between regions can lead to inequality, conflict, and migration. Understanding development geography is essential for promoting equitable and sustainable development that benefits all members of society.
Explain the Methods Used in Human Geography
Human geographers employ a diverse array of methods to gather and analyze data about human activities and their impact on the environment. These methods can be broadly classified into qualitative and quantitative approaches.
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods focus on understanding the subjective experiences and perspectives of individuals and groups. They often involve in-depth interviews, participant observation, and ethnographic research.
- Strengths:Provide rich, detailed data that captures the nuances of human experiences and motivations.
- Weaknesses:Can be time-consuming and subjective, and the results may not be easily generalizable to larger populations.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods emphasize the collection and analysis of numerical data to measure and analyze human activities and patterns. They include surveys, statistical analysis, and remote sensing.
- Strengths:Allow for the collection of large amounts of data that can be analyzed statistically to identify trends and patterns.
- Weaknesses:Can be less detailed and may not capture the complexities of human experiences and motivations.
Examples of Methodological Applications
- Qualitative methods:Ethnographic studies of urban poverty have provided insights into the challenges and resilience of marginalized communities.
- Quantitative methods:Statistical analysis of census data has been used to identify spatial patterns of income inequality and segregation.
li> Mixed methods:A combination of qualitative and quantitative methods has been employed to study the impact of climate change on coastal communities, providing a comprehensive understanding of both the physical and social dimensions of the issue.
Discuss the Challenges Facing Human Geography
In the 21st century, human geography faces numerous challenges that are reshaping the discipline. These challenges stem from technological advancements, globalization, and the increasing complexity of human-environment interactions.
The Data Revolution
The explosion of data available to geographers through remote sensing, social media, and other sources has created both opportunities and challenges. While this data has the potential to provide new insights into human behavior and spatial patterns, it also presents challenges in terms of data management, analysis, and interpretation.
Globalization and Interconnectedness
Globalization has led to increased interconnectedness between different parts of the world, making it more difficult to study human geography in isolation. Geographers must now consider the global context of local phenomena and the ways in which local actions can have global consequences.
Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability
Climate change and environmental sustainability are major challenges facing humanity, and human geographers have a crucial role to play in understanding and addressing these issues. Geographers must develop new ways to study the human dimensions of climate change and identify sustainable solutions.
Social and Political Change, Ap human geography unit 3 frq
Social and political change are also posing challenges to human geography. The rise of populism, nationalism, and other forms of identity politics has made it more difficult to build consensus on how to address global challenges. Geographers must find ways to navigate these complex political landscapes and continue to provide evidence-based research.
Expert Answers
What is the scope of human geography?
Human geography encompasses the study of human societies and their interactions with the physical environment, exploring how these interactions shape cultural, economic, political, and environmental landscapes.
How are the themes of human geography interconnected?
The themes of population, culture, environment, and development are deeply interconnected. Population growth and distribution influence cultural practices, environmental degradation, and economic development. Cultural values shape how humans interact with the environment, while environmental conditions can influence cultural beliefs and practices.
Development processes impact population distribution, cultural norms, and environmental sustainability.
What are some challenges facing human geography in the 21st century?
Human geographers face challenges such as climate change, globalization, urbanization, and resource scarcity. These challenges require geographers to adapt their research methods, collaborate with other disciplines, and engage with policymakers to address complex global issues.